Ambrosia dumosa, White Bursage





Scientific Name: Ambrosia dumosa
Common Name: White Bursage
Also Called: Burro Weed, Burrobush; (Spanish: Chicurilla, Estafiate, Ambrosia, Huizapol, Hierba del Burro, Chamizo)
Family: Asteraceae, Sunflower Family
Synonyms: (Franseria dumosa)
Status: Native
Duration: Perennial
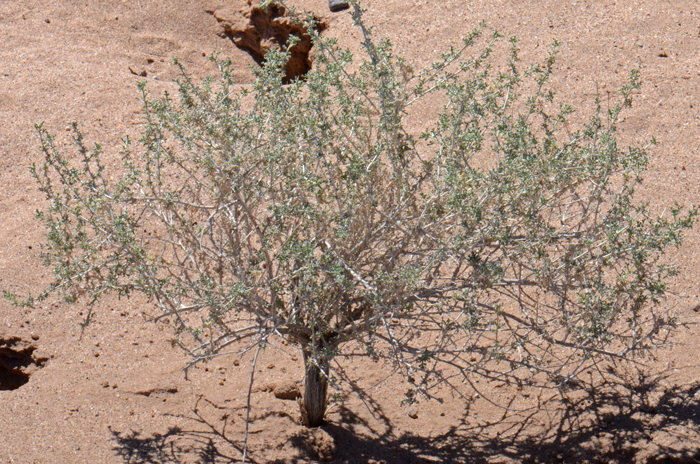
Size: Up to 3 feet (1 m) tall, usually much less (2 feet - .6 m)
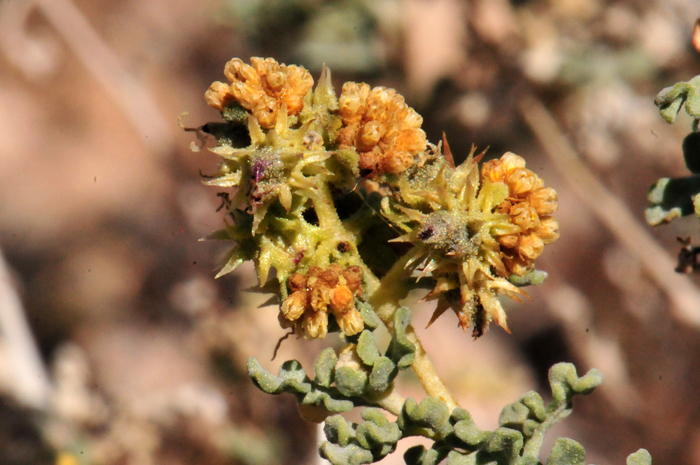
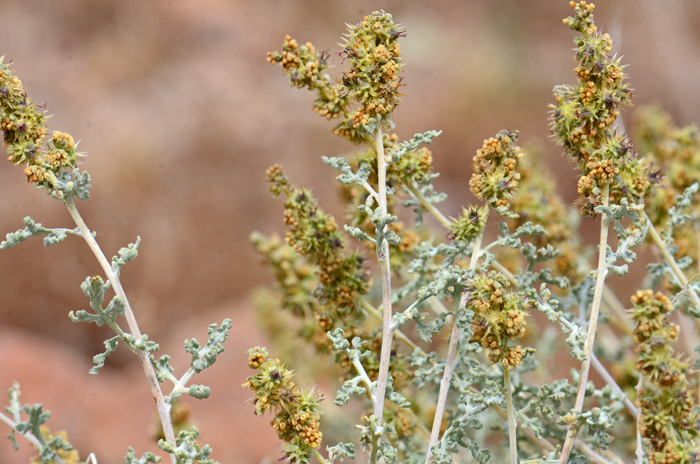
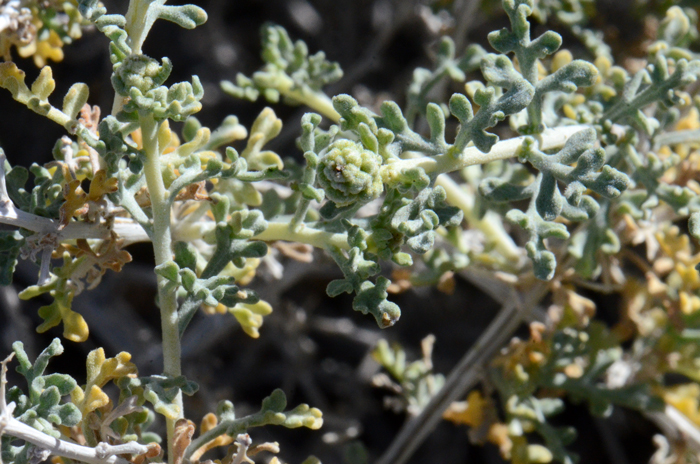
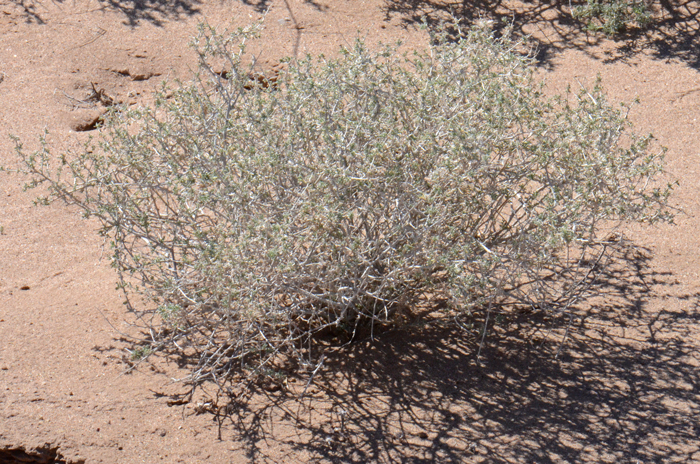
Growth Form: Shrub or subshrub; erect; compact; plants more or less spinescent, whitish color, becoming hairless (glabrous) at maturity; herbage softly canescent to strigose; bark gray.
Leaves: Leaves light gray or whitish; leaves arranged alternately along the stems; leaf blades are elliptic to ovate, 1, 2 or 3 times pinnately lobed; both sides of leaves densely grayish-tomentose.
Flower Color: Green and yellowish; inconspicuous flowers, male (staminate) and female (pistillate) flowers (monecious), male and female flower heads intermixed on raceme inflorescence; fruit is a roundish or spherical spiny bur.
Flowering Season: February, March or April to November or December
Elevation: Below 3,000 feet (914 m)
Habitat Preferences: Common on dry rocky and sandy washes, dry alluvial soils.
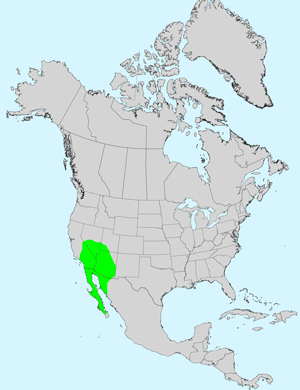
Recorded Range: In the United States, White Bursage is found in AZ, CA, NV and UT but primarily in southeast CA and western AZ. It also grows in northwest Mexico (Sonora) and Baja California. In Arizona it is found mostly in the western half of the state.
North America & US County Distribution Map for Ambrosia dumosa.
North America species range map for Ambrosia dumosa:
North American range map courtesy of Virginia Tech, Dept. of Forest Resources & Environmental Conservation
U.S. Weed Information: Unknown
Invasive/Noxious Weed Information: Unknown
Wetland Indicator: Unknown
Threatened/Endangered Information: Unknown
The genus Ambrosia was published by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
In the Southwestern United States: Arizona has 15 species of genus, California has 14 species, Nevada and New Mexico each have 8 species, Texas and Utah each have 10 species. Data includes Hymenoclea. All data approximate and subject to revision.
Comments: Like other Ragweed, White Bursage is wind pollinated and highly allergenic to people suffering from hay fever. Ambrosia dumosa, although common throughout both the Sonoran and Mojave deserts, is much more predominant in the Mojave Desert. It thrives in alkaline soils and has the ability to withstand very high surface temperatures for extended periods and often looks lifeless.
White Bursage is one of the dominant or co-dominant species in the Sonoran and Mojave Deserts, much more so in the Mojave Desert plant communities. White Bursage thrives in poor alkaline soil conditions and is often found in open bare areas with Creosote Bushes (Larrea tridentata).
White Bursage hybridizes with Cheesebush, Ambrosia salsola. Burro Weed and Burrobush are common names also used for other southwestern plants.
For a comprehensive and thoroughly documented review of White Bursage, Ambrosia dumosa see the USDA USFS Fire Effects Information System, or FEIS.
Also see in Southwest Desert Flora Canyon Ragweed, Ambrosia ambrosioides, Triangle-leaf Bursage, Ambrosia deltoidea, Hollyleaf Bursage, Ambrosia eriocentra, Burrobush, Ambrosia monogyra and Cheesebush, Ambrosia salsola.
Seeds of Ambrosia dumosa may likely be eaten by birds and small mammals; many desert rodents, including kangaroo rats, black-tailed jackrabbits and sheep are known to feed on burrobush seeds.
The species epithet "dumosa" (dumo'sa/dumo'sum:) means bushy or shrubby, references to its growth characteristics.

